Biometric Surveillance Behind the Screen
Authored by: The Center of Biometric Trafficking Awareness
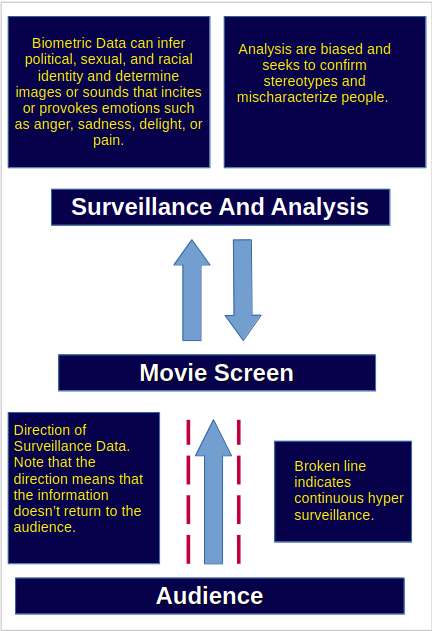
The identity of individuals in movie theaters are being gathered and examined without their knowledge using biometric surveillance. Biometric surveillance is the use of cameras to gather biometric information from individuals. Movie theaters are ideal environment for biometric surveillance because the audience is sitting for hours looking directly at a large screen that would serve as a map for tracking wherever they look and how they react to where their eyes are fixed. Most experts agree that biometric technology that attempts to identify behavior and emotions are erroneous. However, the movie industry are more concerned about the reception of their movies and how these information can influence an individual’s consent. This has led to a practice of surveillance and retaliation. If an individual looks away from an actor, then the industry retaliates by trafficking that individual’s information. In this way, the movie industry has created a surreptitious system of surveillance and retaliation. Biometric surveillance can provide information about an individual’s identity such as their sexual orientation, political beliefs, religious affiliations, and emotions.The movie industry is a business that runs on peoples’ emotions. The emotions of their audience is the key to consent.
Because the surveillance is surreptitious, they are considered unilateral. This is indicated by the arrows in the diagram. That is, the audience is unaware that they are being surveilled while watching a movie. They are also unaware of how their biometric information is being analyzed. Perhaps, this is undisclosed because the results of biometric surveillance are often inaccurate. Biometric surveillance in movies are also continuous. They continue to gather information about an individual during the entire movie. This is indicated by the red line in the diagram. Also, we use the term hyper biometric surveillance for the individualized focus on an individuals’ identity such as their behavior while they watch a film. Hyper biometric surveillance is defined by the fineness of the data being analyzed. This can include how an individual sits on a chair, arm movements, and where they look on the screen during the entire movie. The analysis and gathering of the biometric data is active. This activity is not perceived by the audience.
The Center for Biometric Trafficking Awareness also suspects that the movie industry are seeking to confirm racial and gender biases to confirm stereotypes and characterization found in movies. In this way, bias in representation carries over off the screen. CBTA will continue to investigate the way the movie industry handles private data by means of biometric surveillance.